
For example, a company may be highly leveraged and must therefore make massive interest payments that are not considered part of the operating ratio. Nonetheless, this ratio is commonly used by investors to evaluate the results of a business. In finance, the operating ratio is a company’s operating expenses as a percentage of revenue. Operating expenses encompass all costs except interest payments and taxes. Organizations do not factor in non-operating expenses, such as exchange rate costs, into the operating ratio, as these are extra expenses unrelated to core business activities.
Operating Efficiency Ratios Explained in Video
Also, investors can monitor operating expenses and cost of goods sold (or cost of sales) separately to determine whether costs are either increasing or decreasing over time. Operating profit ratio, also known as operating margin ratio, refers to the amount of money earned by a company through its operations expressed in percentage terms. It shows how much it costs for a company to make one dollar of revenue. big tax changes for musicians in 2018 This metric is especially useful when comparing profitability among different companies or industries with varying cost structures. In its essence, the operating margin is how much profit a company makes from its core business in relation to its total revenues. This allows investors to see if a company is generating income primarily from its core operations or from other means, such as investing.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
This signals to investors that the business model is effective at producing earnings from its central operations. On the other hand, a higher operating ratio indicates high operating costs are eroding profitability, which is a red flag for lower-quality earnings and cash flows. Examine multi-year trends in the company’s operating Ratio to assess historical operational leverage. The operating Ratio is calculated as operating expenses divided by net sales or sometimes as operating expenses divided by gross profit. A declining ratio over time indicates the company is gaining operating leverage – meaning revenues are growing faster than operating costs, leading to expanded profit margins. This demonstrates management’s ability to control costs amid business growth and suggests future margins could continue improving with scale.
How Can Companies Improve Their Operating Profit Margin?
Certain items such as goods returned are deducted from the gross sales to find net sales.
- In other words, it indicates how efficiently management uses labor and supplies in the production process.
- This analysis provides crucial insight into the risks and opportunities facing the business.
- The ratio helps to analyze trends and track performance over a certain period.
- This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
- In other words, this means that for every $1 in assets, the firm is able to generate $1.17 in revenue.
Investors must dig deeper to understand inflections in the operating ratio trendline. A high turnover ratio, and thus a low DOH ratio, may mean that the firm isn’t keeping enough inventory on hand. A low turnover ratio, and a high DOH ratio, may mean the firm is having issues selling the inventory. These ratios often point toward other problems in the firm, and are used as a starting place. If turnover is low, one may want to look into the company further to find out why.
The denominator should be a company’s net sales or revenue over the defined time interval. This represents the total top-line sales or revenue after adjustments for returns, discounts, and allowances. Net sales captures the true volume of goods and services sold to customers. Special items or one-time events that cause sudden changes in operating Ratio reveal issues like production bottlenecks, supply chain problems, lawsuits, or restructuring costs.
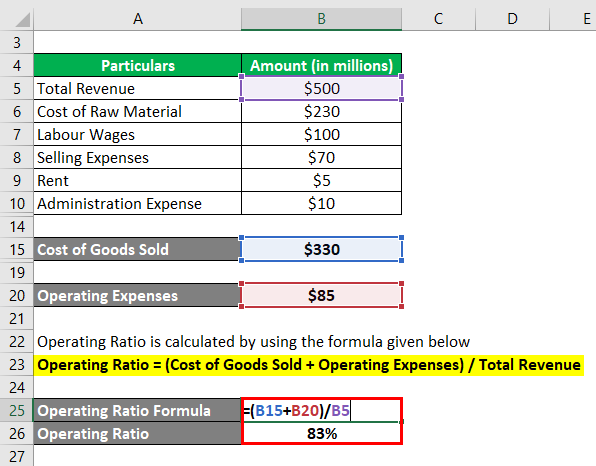
A negative operating ratio signals poor profitability, as the company is losing money on its core business operations. For stock investors, a negative operating ratio would be a red flag that a company needs to cut costs or boost sales to avoid further losses and improve its financial performance going forward. The operating ratio formula is the ratio of the company’s operating expenses to net sales.
Products and services drive a company’s competitiveness and reputation. Skimping on quality could lead to defections, lawsuits, and other blows to the brand. Similarly, unsustainably suppressing expenses like R&D or wages temporarily boosts margins but leaves the business exposed. Beyond operating Ratio, investors should also look at key performance indicators like revenue growth, market share changes, return on invested capital, cash flows, and balance sheet strength. The objective is to find well-run businesses with solid competitive advantages and growth prospects. In other words, this means that for every $1 in assets, the firm is able to generate $1.17 in revenue.


التعليقات مغلقة.